
Media Conversion
Choosing the right backbone
- By Susan Stanley
- Jun 01, 2014
 When a successful European toy
manufacturer outgrew its facilities,
it built a new, three-facility
campus that included an
office along with manufacturing
and warehouse space. It would have been impractical
to network the new campus with copper Ethernet
cable, since it has a range limitation of about 100
yards. While that could have been increased to 1,900
yards with Ethernet extenders and DSL technology,
the bandwidth would have been limited at the longer
ranges. Instead, the manufacturer chose multi-mode
fiber as the network backbone.
When a successful European toy
manufacturer outgrew its facilities,
it built a new, three-facility
campus that included an
office along with manufacturing
and warehouse space. It would have been impractical
to network the new campus with copper Ethernet
cable, since it has a range limitation of about 100
yards. While that could have been increased to 1,900
yards with Ethernet extenders and DSL technology,
the bandwidth would have been limited at the longer
ranges. Instead, the manufacturer chose multi-mode
fiber as the network backbone.
Multi-mode is less expensive than single-mode fiber
as it typically employs lower-cost electronics, like
LEDs and vertical cavity surface emitting lasers (VCSELs).
It has a smaller range than single-mode fiber,
which can reach up to 64 miles, but multi-mode can
still carry data several miles at speeds of up to one
Gigabit. Multi-mode shares single-mode fiber’s immunity
to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI), and
both fiber types are inherently secure because the data
travels on a beam of light, meaning outsiders can’t
hack in via Wi-Fi.
Security was an important consideration since
the facility received daily visits from toy sales representatives,
vendors and other outsiders. The factory
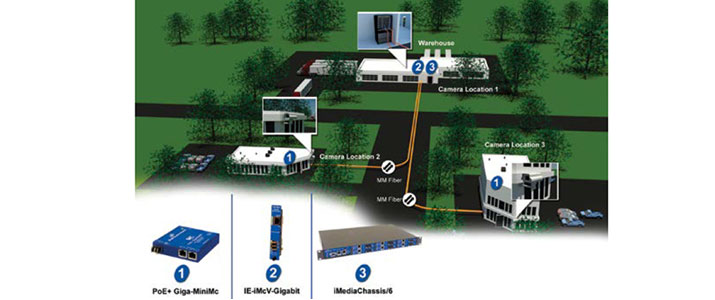
owners wanted to establish 24/7 video surveillance
for the campus, but IP cameras are typically installed
in inconvenient locations—you’ll see them on top of
light poles, for example. These cameras need a power
supply of some sort, and because IP cameras usually
have 100 MBps copper interfaces, they would also
need media conversion before they could connect to
the campus’ fiber infrastructure.
Standard copper-to-fiber media converters could
convert the signals from IP cameras, but they wouldn’t
solve the power problem. And, because the cameras
would be outdoors, the company needed media converters
with extended temperature specs, along with
the ability to observe and report faults on remote copper
and fiber connections.
The manufacturer ultimately chose a PoE media
converter, the B&B Electronics PoE+ Giga-MiniMc.
Power over Ethernet (PoE)
While concurrently supporting the Ethernet data
stream, PoE devices greatly simplify installation by
letting network switches and other “injectors” provide
power to connected devices over the Ethernet cable.
This works because a copper RJ-45 cable has four
wires: Two support the data stream, and the other
two are available for PoE. A PoE copper port’s ability
to carry power will not impact or reduce the efficacy
of the data stream. Low-power devices can use Cat-3
cables, but devices that draw more power require Cat-
5, Cat-5e or Cat-6 cables.
There are two types of PoE power sourcing equipment
(PSE) that support point-to-multipoint power
distribution: endspan and midspan. An endspan PSE
is typically a switch and can be placed anywhere a
switch or router would normally be required. Midspan
devices, like PoE-enabled media converters, inject
power inline and are often used when upgrading
an existing network to PoE standards. A midspan device
is placed between an existing legacy switch and a
powered device, which could be an IP camera, a wireless
access point, a serial device server or any other IP
device that requires power.
On initial power up, the PSE is designed to detect
and supply power to only the network devices that it
identifies as being PoE-enabled. The PSE initiates this signature detection process by using low
probing voltages to sense the type of
connected power device. PSEs are able
to detect several undesirable load conditions,
including shorted communications
cables, disconnected powered devices
and the connection of non-PoE devices.
The original IEEE 802.3af-2003
PoE standard provided up to 15.4
W DC—minimum 44 V DC and 350
mA—to each device, with 12.95 W
available at the powered device after
cable loss. But some devices, such as
heated remote cameras, need more.
So, the newer IEEE 802.3at-2009 PoE
standard (referred to as either PoE+ or
PoE plus) nearly doubles the available
power, providing up to 25.5 W while
remaining compatible with the older
802.3af PoE standard.
PoE+ switches and injectors will
recognize 802.3af powered devices and
source power to them accordingly. The
reverse is also true: PoE+ powered devices
will recognize 802.3af PoE injectors
and are designed to restrict how
much power they draw, preventing
damage to the equipment.
With PoE’s low voltage, it is considered
to be safe enough that it doesn’t
bring strict building codes into play,
which lowers installation costs. Note
that AC power standards, plugs and
outlets vary from one region to another,
but PoE equipment works everywhere.
Hot Swappable Transceivers
and Remote Diagnostics
In addition to the twin 10/100/1000
MBps PoE copper ports, the media
converters provided a small form pluggable
(SFP) fiber port. SFP fiber ports
future proof an installation by supporting
both 100 MBps and 1000 MBps connections.
Currently, the toy factory only
requires 100 MBps connectivity to meet
its needs. If, at a later date, the owners
wish to upgrade the system to gigabit
(1,000 MBps), the transition from multimode
to single-mode fiber would be
easy. There would be no need to replace
the media converters; the hot swappable
SFP transceiver is the only component
that would need to be changed.
The media converters provide a useful
diagnostic feature called Link Fault
Pass Through (LFPT). LFPT means
that the state of the 100BASE-TX copper
receiver is passed to the 100BASEFX
fiber transmitter. Imagine a situation
in which a remote device stops
communicating. The LFPT function lets
the media converter detect the lost copper
link and alert the network manager.
By deploying devices that combine
PoE, remote management features and
wide temperature specs, this toy manufacturer
was able to establish video surveillance
in all desired locations while
simultaneously retaining the option to
upgrade to single-mode fiber, should
the need arise.
This article originally appeared in the June 2014 issue of Security Today.