In The Zone
Retail outlets must ensure they are abiding by regulations
- By Mike Lloyd
- Jun 22, 2009
A delicate balance exists in the retail world as businesses try to ensure easy and seamless customer experiences while maintaining high security. This ranges from finalizing a transaction, down to information security controls and processes designed for data integrity. A business must ensure it is abiding by industry and government regulations as well as providing a secure and protected environment for the transfer and storage of personal customer data.
Achieving a reasonable state of security has been, for many, a difficult objective as application uptime often takes a front seat over other initiatives. However, when IT security needs are expressed in terms of meeting compliance requirements, such as the Payment Card Industry’s data security standard, executives and top-level business managers take notice.
Networks are complex entities, with many moving parts. Determining how to align security practices with other efforts to meet an organization’s needs appears to be a monstrous task. Auditing the setting of each knob and dial on every low-level network device may sound sensible, but such an approach is equivalent to assessing patterns in the bark of trees while ignoring the trees themselves and the forest altogether. Knowing what traffic is permitted and what must be blocked is necessary. But this is inherently an end-to-end question, not a device configuration question.
Compliance Objectives
There’s a clear advantage in converging the goals of all the various compliance objectives. It centers on scope. Anyone manually measuring compliance today will tend to reduce the scope of the project as much as possible. However, this point flips around if automation is applied. The more an organization can automate the management of firewall and router configurations, the more the objective shifts from small scope to unified scope. An organization also should test the whole regulated infrastructure regularly, from a single viewpoint of what is and what it not permitted.
The ideal target is a single set of tools and processes for compliance, evaluated against an infrastructure, with a specific set of rules outlining what is compliant. Reaching this ideal isn’t trivial, but in a world where compliance burdens are continuously increasing, it is a critical survival strategy to unify and automate this work as much as possible. The most successful organizations are well along this path, finding commonality across regulation sets, and applying fixed standards in a turn-key fashion. The contrast in efficiency is stark between these teams. For those in reactive mode, struggling to clear each different regulatory milestone is an isolated project.
As a company looks to better align its security practice with its assessment practice, it has to examine firewall rule sets. Some companies attempt a brute-force approach, building a database of every single rule in every firewall, identifying the owner of each line and re-approving every rule on a regular basis. While logical, such a practice is untenable, despite following the regulations.
People can’t reliably review thousands of complex firewall policy statements. Even if they could, it takes too long for the business to see its benefit. Instead, there’s a deeper issue in this device-by-device approach. Even if one could validate every rule in every firewall, the outcome would not lead to a better understanding of a company’s overall network defensive posture. The complexity of many networks is staggering, as they often include remote sites, each with their own firewalls and VPN equipment. The number of interactions required to ensure a network is operational is staggering.
A New Approach
Leading IT security managers are stepping back from the idea of auditing everything. Instead of managing every rule in every firewall within a database, a more reasonable approach involves managing groups or zones of activity. A company may break its network into a variety of groups, including Internet, extranet, customer database, ERP system and wireless areas. A matrix could represent each group and every legal type of traffic between the various areas in a zone-based, rather than rules-based, approach to security management.
It would be unwise to create a large matrix of dozens or hundreds of cells. To address PCI requirement No. 1, for example, the creation of a four-by-four matrix would work well (see diagram).
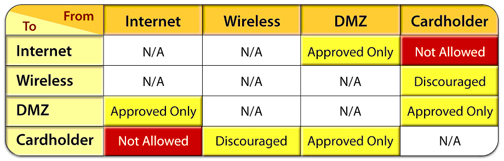
PCI-DSS requirement 1, allowable traffic by zones
A zone matrix provides a common language with which to communicate issues and exposures. It is critical that zone-to-zone relationships make sense to people within the organization who are not on the security team. Without that comprehension, necessary resources for getting security issues resolved will not be assigned.
The next step, after taming the complexity through zone management, is to automate the compliance assessment process by using a computer to analyze firewall and router configurations across the entire network. Through automation, security teams are finding forgotten severs attached to networks with access connections to other servers creating security holes. They are finding mistakes and omissions within router access or firewall rules that create problems.
The ability to scale and better manage a network to meet compliance requirements, as well as continually improve the company’s security posture within a complex, rapidly changing IT infrastructure is within reach. Through automation, security teams are regaining valuable time and increasing accuracy.
About the Author
Mike Lloyd is the chief scientist at RedSeal Systems Inc.