Invasion of the Body Scanners
Some say airport security technology now reveals too much
- By Ronnie Rittenberry
- Dec 01, 2010
The blogosphere lit up in mid-October
when Michael Roberts, a pilot for
Houston-based ExpressJet Airlines
Inc., refused to submit to a full-body scan or
a manual pat down at Memphis International
Airport. At issue were the advanced imaging
technology (AIT) scanners the airport had
only recently installed in place of traditional
metal detectors at security checkpoints,
manned by employees of the Transportation
Security Administration. Roberts said the
new system was intrusive, invaded his privacy,
and violated his constitutional rights against
unreasonable searches and seizures by government
agents.
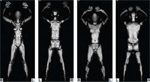
“These devices enable screeners to see
beneath people’s clothing to an extremely
graphic and intrusive level of detail (virtual
strip searching),” Roberts wrote in a post to
The Pipe, an online forum for aviation professionals.
“Travelers refusing this indignity may
instead by physically frisked by a government
security agent until the agent is satisfied to
release them on their way in what is being
touted as an ‘alternative option’ to AIT.”
Portal-bility
The technology, which TSA began selectively
deploying in 2007, is designed to detect metallic
and non-metallic threats -- think plastic
and liquid explosives that evade metal detectors.
It requires passengers to step into a
9-foot-tall glass-walled portal that bounces
millimeter waves off their bodies to create a
metallic-looking image that screeners view on
a monitor in a closed room. The process takes
a little longer than metal-detector screenings
of yore and yields images that undeniably
leave little to the imagination.
Responding to a pro-AIT blog on the
TSA website, one commenter countered
that the images expose “passengers’ bodies
in sufficient detail for screeners to count the
change in our pockets and see beads of sweat
on our backs -- not to mention intimate, gender-
specific details.”
Importantly, TSA says individual faces are
blurred and the images are deleted as soon as
a passenger is cleared through a checkpoint,
but this is an aspect of the system critics simply
aren’t buying. On its blog (at http://blog.
tsa.gov), TSA notes that the AIT machines do
have USB, hard disc, and Ethernet capabilities --
and that in “test mode” the machines
definitely have the ability to store, export,
and print images -- but the agency insists that
this functionality is “disabled” before the machines
are delivered and that there is no way
for the on-site TSA employees to place them
back into test mode.
Invariably, skeptics have focused on the
agency’s use of the word “disabled” as opposed
to “removed” and, in the comments
section of TSA’s blog, written things such as,
“Any function that is disabled can be reenabled
at some future time.”
“If there’s a way for someone else to put
the machine into test mode, then there’s a
way for an unauthorized person to do so,
too. That’s how security holes happen.”
“A tech-savvy person with physical access
to a computer can make it do almost anything.”
And,
“So just how does this technology prevent
an operator from taking a picture of the
screen?”
Balancing Beams
The safety of the technology has been another
source of contention. TSA maintains that the
millimeter waves -- essentially low-level X-ray
beams -- are harmless. But not so fast, critics
protest. The technology has not been around
long enough for anyone to say with scientific
certainty just how innocuous or dangerous
those waves might be -- especially on pilots,
who would be exposed to them on an overly
regular basis, potentially several times a day.
These concerns notwithstanding, all indicators
point to AIT being the wave of the
future. TSA already has installed 300 of the
machines at some 60 airports nationwide and
plans to deploy 150 more of the $150,000
units by the end of 2010. An additional $88
million is included in the 2011 national fiscal
budget for 500 more machines.
On Oct. 22, one week to the day after Roberts’
run-in with TSA in Memphis, Department
of Homeland Security Secretary Janet
Napolitano was on hand at JFK in New York
for the unveiling of the first of a “substantial”
number of the machines that will be installed
at that airport. Hailing them as a significant
breakthrough for airport security and the fight
against terrorism, she said, “These machines
represent an important way to stay ahead of
the ever-evolving threat that faces the aviation
industry.” According to the New York Daily
News, though, when it came time to demonstrate
how the machines work, the secretary
opted to allow others to step in the portal.
Meanwhile, as of press time, Roberts has
not worked as a pilot since TSA sent him
home on Oct. 15.
“So right now, despite management’s
strong desire to impale me in front of all my
coworkers lest any of them decide to follow
my example, the company’s lawyers have advised
them to accept my offer to take a leave
of absence until my issues with the federal
government are resolved and I am able to
return to the skies as a free citizen,” Roberts
wrote on Oct. 29, in response to an e-mail inquiring
about the outcome of his Memphis
ordeal. “My battle with them is far from over,
though. But at least it’s on a back burner for
the time being.”
This article originally appeared in the issue of .
About the Author
Ronnie Rittenberry is print managing editor for Security Products and Occupational Health and Safety magazines.