When conducting a review of how a service provider will handle personal information for this or that process, the subject inevitably turns to the protection of the personal information involved. Often it is said that everything should be fine; the vendor passed the security review and the confidentiality clause is airtight. While these things are good and important and are positive statements about information protection, management, and recourse in the event it is needed; they are not answers as to how the personal information will be protected; i.e.; how privacy will be managed.
The reason for this is the goals and requirement of privacy are not entirely the same as those of information security or those of confidentiality. As such, it is important not to confuse one for the other. In fact, doing so may create risk rather than mitigate it.
So, how is data privacy different from information security and from confidentiality? How are they alike? How they are alike is easy to answer. They are all forms of information protection. Beyond that it is easier to understand how they overlap by understanding how they are different.
Let’s start with definitions.
Privacy is the fair and authorized processing and access of personal information. Note there are many definitions of privacy. This is an operational definition.
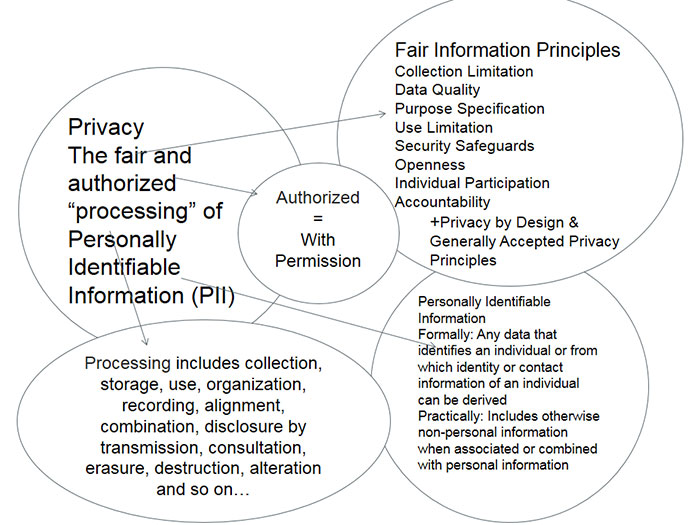
Personal information is any information that can be used to identify or contact an individual or be reasonably linked to a specific individual, device or computer.
Processing is any action or inaction that can be performed in relation to that data or dataset. Processing personal information includes, but is not limited to, collection, storage, use, sharing, organization, display, recording, alignment, combination, disclosure by transmission, copying, consultation, erasure, destruction, and alteration of personally identifiable information and any data related to it.
Fair and authorized includes notions of the ideas embodied in the Fair Information Practice Principles or the OECD Privacy Guidelines such as collection limitation, data quality, purpose specification, use limitation, security safeguards, openness, accountability, and individual participation.
Information Security is that the use of logical, technical, administrative, physical safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data is maintained.
Confidentiality is preventing authorized access to non-public information that two or more parties have agreed to restrict.
The Overlaps
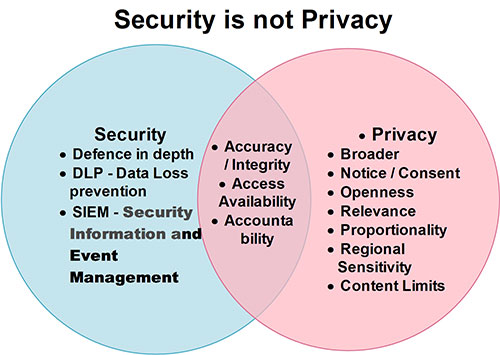
Information Security safeguards ensure the “authorized” in the “authorized access and use” that is a cornerstone the operational definition of privacy. This is why one cannot have privacy without security. Note, though one can have security without privacy (which is one of the major disconnects) where personal information is not involved.
Three other areas of overlap between privacy and information security:
- Integrity (Information Security) and Accuracy (Privacy)
- Information security’s integrity requirement overlaps with privacy’s accuracy requirement in that both target ensuring that the data are not altered without both authentication and authorization
- Availability (Information Security) and Access (Privacy)
- Information security’s availability requirement supports privacy’s access requirement because if the data is not available, it cannot be accessed
- Accountability (both)
- Both information security and privacy doctrines require data owners and custodians to be responsible for protecting the data in accordance with the respective protection regimen, which is a form of accountability
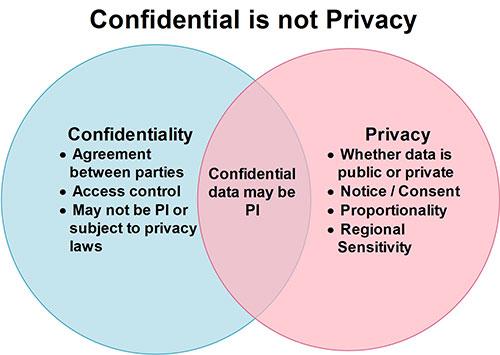
Confidentiality overlaps when the information being identified as “confidential” is both personal information and nonpublic because nonpublic data need to be kept nonpublic.
Unfortunately, confidentiality does not help much if the data in question is “public.”
The Disconnects
First let’s look at the disconnects between Privacy and Information Security. The reason there is not a complete overlap between privacy and information security is threefold.
First, privacy has a wider set of obligations and responsibilities than information security does, such as:
- Collection limitation – simply put, there are limits to how data can acceptably be collected; that the collection must be fair and lawful and, where possible, with the individuals consent.
- Openness – This means there should be transparency about an organization’s processing of personal information.
- Relevancy – The data collected should be proportional and appropriate for the purpose of the processing.
- Use limitation – the personal information should not be used for purposes other than those specified when the data was collected without additional permission.
This means there are things privacy addresses that information security does not.
The second disconnect is confidentiality. Because personal information (PI) is not always nonpublic (consider the phonebook), the notion of confidentiality does not apply. Also, in a resource-constrained world, if the data are not considered confidential, they are not always “valued” and the necessary measures to ensure authorized access and use will be overlooked.
Third, and perhaps most important, while information security techniques can be privacy-enabling technologies (PETs) (which means they are tools that enable privacy) and are often necessary, these PETs can also become “feral” if applied incorrectly (i.e. in an invasive manner). As mentioned above, this is why one can have security without privacy, but one cannot have privacy without security.
As for confidentiality, as mentioned above, confidentiality rules only apply to what is designated by agreement as confidential. This is the first difference between confidentiality and privacy. Confidential is an imposed label that signifies access control. PI is an organic label; it speaks to the substance of the information. Just as with that famous line in Shakespeare’s immortal play Romeo and Juliet “A rose by any other name would smell as sweet,” so it goes with PI. It’s always going to be personal information when it identifies an individual.
Sometimes confidential information is also personal information. This is when the concepts overlap. Other times, for instance when the information is publically available, the notions of confidentiality miss the mark. Whereas public information – even public personal information -- is free of confidentiality requirements, it is not free of privacy requirements. One example of this is e-marketing lists. Many of our e-mail address are publically available, but that does not mean they can be wantonly maintained on e-marketing lists without our permission.
So What Does This Mean?
First and foremost, it is important to understand the difference between information security, confidentiality, and privacy. It is at one’s (or one’s organization’s) peril to substitute one for the other. It means that there is a rich tool set with which to protect information (including personal information), but that it is important for all practitioners of data protection – IP attorneys, Information Security Specialist, and Privacy Professionals – need to be mindful of the data in question and insure the proper protection paradigm is applied.